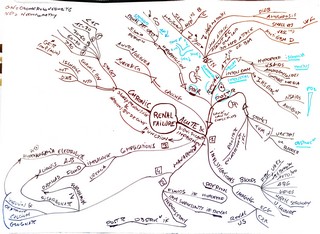
(Medimaps) Renal Failure
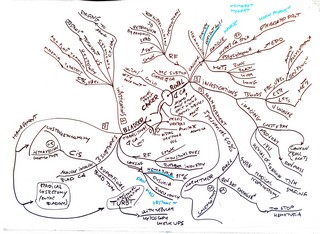
(Medimaps) Renal & Bladder Cancers
| NEWS & UPDATES | MAPS |
REFERENCES |
| EMBRYOLOGY | ANATOMY | HISTOLOGY | PHYSIOLOGY | PATHOLOGY | PHARMACOLOGY |
| ACID-BASE | ELECTROLYTE |
| GLOMERULAR |
STONES | INFECTION | CYST |
TUMORS |
| MAPS |
| CONTENTS |
| INTRODUCTION The kidney: structural overview The kidney: functional overview Development of the renal system Clinical features of kidney disease The kidney: laboratory investigation and diagnostic imaging |
| EMBRYOLOGY |
| RENAL DEVELOPMENT - KIDNEY EMBRYOLOGY |
|
Filtration system (nephron) Collecting system |
| CONGENITAL ABNORMALITIES |
| POTTER SEQUENCE Babies who can’t “Pee” in utero develop Potter sequence POTTER sequence associated with: Pulmonary hypoplasia Oligohydramnios (trigger) Twisted face Twisted skin Extremity defects Renal failure (in utero) RENAL ECTOPY HORSESHOE KIDNEY CONGENITAL SOLITARY FUNCTIONING KIDNEY Unilateral renal agenesis Multicystic Dysplastic Kidney DUPLEX COLLECTING SYSTEM POSTERIOR URETHRAL VALVE VESICOURETERAL REFLUX |
| ANATOMY |
| RENAL BLOOD FLOW |
| GLOMERULAR ANATOMY |
| POSTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL |
| RETROPERITONEAL STRUCTURES |
| Kidney Ureters Course of ureters Bladder Prostate Urethra Male Urethra Female Urethra |
| HISTOLOGY |
| NEPHRON |
| Renal Corpuscle Glomerulus Bowman Capsule Tubular System Proximal Convoluted Tubule Loop of Henle Distal Convoluted Tubule Collecting Tubules Collecting Ducts Cortical Versus Juxtamedullary Nephrons |
| JUXTAGLOMERULAR APPARATUS - JGA |
| Macula Densa (NaCl sensor located at the DCT) Juxtaglomerular (Granular) Cells - JG Cells (Modified smooth muscle of afferent arteriole) Intraglomerular Mesangial Cells Extraglomerular Mesangial Cells |
| RENAL CALYCES, RENAL PELVIS, & URETERS |
| BLADDER |
| PHYSIOLOGY |
|
|
| CONCEPTS OF TRANSPORT |
| DEFINITIONS Quantity Concentration FORMS OF TRANSPORT Concepts of Transport Transcellular transport Paracellular transport Passive Transport Simple diffusion Facilitated diffusion Nonionic diffusion Osmosis Osmotic pressure Active Transport Primary active transport Secondary active transport Cotransport (symport) Countertransport (antiport) Rate-Limited Transport FLUID COMPARTMENTS Composition of Extracellular Fluid and Intracellular Fluid HIKIN’: HIgh K+ INtracellularly ESTIMATING AND MEASURING FLUID COMPARTMENT VOLUME Estimating Body Fluid Volumes Measuring Body Fluid Volumes INTERCOMPARTMENTAL WATER DYNAMICS ECF PATHOPHYSIOLOGY KEY FACTS Iso-osmotic volume contraction Hypo-osmotic volume expansion |
| GENERAL RENAL PHYSIOLOGY |
| RENAL CLEARANCE: GENERAL CONCEPTS Renal Clearance (Cx) GLOMERULAR FILTRATION BARRIER Fenestrated capillary endothelium Glomerular basement membrane (GBM) - Basement membrane with type IV collagen chains and heparan sulfate Podocytes - Visceral epithelial layer consisting of podocyte foot processes (FPs) Glomerular Filtrate Glomerular Filtration Rate - GFR Inulin Creatinine RENAL BLOOD FLOW REGULATION MECHANISMS Influencing Factors Sympathetic nervous system Prostaglandins/bradykinin Angiotensin II Dopamine AUTOREGULATION MECHANISMS - RENAL BLOOD FLOW AUTOREGULATION Stretch mechanism - Myogenic Tubuloglomerular feedback mechanism MEASUREMENT OF RENAL PLASMA AND BLOOD FLOW Renal Plasma Flow True Renal Plasma Flow - Effective renal plasma flow Renal Blood Flow Filtration Fraction - FF Changes in Filtration Fraction Changes in glomerular dynamics Calculation of reabsorption and secretion rate CONCEPTS OF REABSORPTION AND SECRETION Glucose - Glucose clearance Amino Acids Urea Para-Aminohippuric Acid Free Water Urine Osmolarity NEPHRON -TRANSPORT- PHYSIOLOGY AND THE TUBULAR SYSTEM Glomerulus Proximal Tubule - Early PCT Loop of Henle Thin descending limb loop of Henle Thin ascending limb loop of Henle Thick ascending limb is a diluting segment Early Distal Convoluted Tubule - Early DCT Late Distal Tubule and Collecting Ducts - Collecting tubule Countercurrent Multiplier System Countercurrent Exchanger (Vasa Recta) RENAL TUBULAR DEFECTS Order: Fanconi’s BaGeLS Hereditary disorders of tubular transport Fanconi syndrome Bartter syndrome Gitelman syndrome Liddle syndrome Syndrome of Apparent Mineralocorticoid Excess Relative concentrations along proximal tubule KIDNEY ENDOCRINE - HORMONE- FUNCTIONS Erythropoietin Vitamin D: Formation of 1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol in the Kidneys - Calciferol (vitamin D) Prostaglandins Dopamine HORMONES ACTING ON THE KIDNEY Atrial Natriuretic Peptide Parathyroid Hormone Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Renin ACE AT II ANP, BNP ADH (vasopressin) Aldosterone Aldosterone Antidiuretic Hormone Potassium shifts |
| ACID-BASE HOMEOSTASIS |
| ACIDS AND BASES Acids Bases Buffers ACID PRODUCTION Volatile Acid Nonvolatile Acid PHYSIOLOGIC BUFFERS Intracellular Buffers Proteins Organic phosphates Extracellular Buffers Major Minor ACID-BASE HOMEOSTASIS Buffer Systems Physiologic pH Acidemia versus acidosis Alkalemia versus alkalosis ACID-BASE HOMEOSTASIS: THE KIDNEY Renal production of H+ and HCO3– Secretion of H+ Secretion as H2PO4– Secretion as NH4+ Reabsorption of HCO3– ACID-BASE HOMEOSTASIS: THE LUNGS Compensation states Metabolic alkalosis Metabolic acidosis Derangement states METABOLIC ACIDOSIS/ALKALOSIS Metabolic Acidosis Metabolic Alkalosis RESPIRATORY ACIDOSIS/ALKALOSIS Respiratory Acidosis Respiratory Alkalosis ACID-BASE CLINICAL IMPLICATIONS Acid-Base Nomogram ACID-BASE PROBLEM SOLVING Acidosis and alkalosis Renal tubular acidosis |
| PATHOLOGY |
| (Le FA 1 Pathology) V1 PDF |
 (Medimaps) Renal Failure |  (Medimaps) Renal & Bladder Cancers |
| URINARY CASTS |
| Epithelial cell casts RBC casts WBC casts Hyaline casts Granular casts Fatty casts (“oval fat bodies”) Waxy casts |
| GLOMERULOPATHIES |
| Nomenclature of glomerular disorders Focal Diffuse Proliferative Membranous Primary glomerular disease Secondary glomerular disease |
| NEPHRITIC SYNDROME Inflammatory process - inflammatory damage to the glomeruli |
| ETIOLOGY Glomerular inflammation > GBM damage > loss of RBCs into urine > dysmorphic RBCs, hematuria CLINICAL PRESENTATION Hematuria Oliguria and azotemia Hypertension EXAMPLES Infection-associated glomerulonephritis - Formerly called post-infectious glomerulonephritis - Acute Proliferative Glomerulonephritis (Poststreptoccocal/Infectious) Children group A streptococcus Adults staphylococcus IgA nephropathy (Berger disease) Rapidly Progressive (Crescentic) Glomerulonephritis Linear IF : Goodpasture syndrome - Antiglomerular Basement Membrane Disease Negative IF/Pauci-immune : Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis Granular IF—PSGN or DPGN Diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis - DPGN Alport syndrome - Hereditary Nephritis Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis - MPGN Type I Type II |
| NEPHROTIC SYNDROME Massive prOteinuria (> 3.5 g/day) - increased filtration barrier permeability |
| ETIOLOGY Podocyte damage > impaired charge barrier > proteinuria CLINICAL PRESENTATION Massive proteinuria Hypoalbuminemia Edema Hyperlipidemia Hypercoagulability EXAMPLES May be 1° (eg, direct podocyte damage) or 2° (podocyte damage from systemic process) : Minimal change disease (1° or 2°) Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (1° or 2°) Membranous nephropathy (1° or 2°) Amyloidosis (2°) Diabetic glomerulonephropathy (2°) Diffuse Membranous Glomerulopathy Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis |
| NEPHRITIC-NEPHROTIC SYNDROME |
| ETIOLOGY Severe GBM damage > loss of RBCs into urine + impaired charge barrier >hematuria + proteinuria CLINICAL PRESENTATION EXAMPLES Can occur with any form of nephritic syndrome, but is most common with : Diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis |
| NEPHROPATHIES ASSOCIATED WITH SYSTEMIC DISORDERS |
| Diabetic Nephropathy Renal Amyloidosis Lupus Nephritis | Hypertension: causes and clinical evaluation Hypertension: complications and therapy Pregnancy and the renal system Diabetes mellitus and the kidney |
| RENAL STONES (UROLITHIASIS) |
| Calcium oxalate stones Calcium phosphate stones Struvite (magnesium ammonium phosphate) stones Uric acid stones Cystine stones |
| Hydronephrosis Urinary incontinence Stress incontinence Urgency incontinence Overflow incontinence |
| URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS |
| Acute cystitis Acute Pyelonephritis Chronic Pyelonephritis Xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis |
| DIFFUSE CORTICAL NECROSIS |
| RENAL PAPILLARY NECROSIS |
| ACUTE AND CHRONIC KIDNEY INJURY |
| Acute Kidney Injury - AKI Prerenal azotemia Intrinsic renal failure Postrenal azotemia Acute interstitial nephritis - TUBULOINTERSTITIAL nephritis Remember these 5 P’S: Pee (diuretics) Pain-free (NSAIDs) Penicillins and cephalosporins Proton pump inhibitors RifamPin Sulfa drugs Acute Tubular Necrosis Chronic Renal Failure - and kidney function in the elderly - CKD Consequences of Renal Failure Consequences (MAD HUNGER) : Metabolic Acidosis Dyslipidemia (especially ↑ triglycerides) High potassium Uremia Ure-PEAN Na+/H2O retention (HF, pulmonary edema,hypertension) Growth retardation and developmental delay Erythropoietin deficiency (anemia) Renal osteodystrophy |
| CYSTIC KIDNEY DISEASE - RENAL CYST DISORDERS |
| Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Autosomal Recessive (Childhood) Polycystic Kidney Disease Autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney disease - medullary cystic kidney disease Simple vs complex renal cysts |
| RENOVASCULAR DISEASE |
| INHERITED RENAL SYNDROMES |
| Fanconi Syndrome Bartter Syndrome Gitelman Syndrome Liddle Syndrome |
| TUMORS OF THE RENAL SYSTEM |
| Renal Cell Carcinoma Clear-cell carcinomas Papillary renal cell carcinomas Chromophobe renal carcinomas Renal oncocytoma Transitional Cell Carcinomas Wilms Tumor (Nephroblastoma) Neuroblastoma Urothelial carcinoma of the bladder Squamous cell carcinoma of the bladder |
| ELECTROLYTE ABNORMALITIES |
| SODIUM AND WATER Sodium Hypernatremia Hyponatremia POTASSIUM Hyperkalemia Hypokalemia DIVALENT IONS – CALCIUM, PHOSPHATE AND MAGNESIUM Calcium Hypercalcemia Hypocalcemia Magnesium Hypomagnesemia Phosphate Features of renal disorders |
| PHARMACOLOGY |
| DRUG AND ORGANIC MOLECULE HANDLING BY THE KIDNEY |
| DIURETICS |
| Diuretics site of action Osmotic Agents (Mannitol and Urea) Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors (Acetazolamide) Loop Agents (Furosemide, Bumetanide, Torsemide and Ethacrynic Acid) Thiazide Diuretics (Hydrochlorothiazide and Metolazone) Potassium-Sparing Agents (Spironolactone, Eplerenone, Amiloride, and Triamterene) Diuretics: electrolyte changes Urine NaCl Urine K+ Blood pH Urine Ca2+ |
| ANTIDIURETIC HORMONE (ADH) (VASOPRESSIN AND DESMOPRESSIN) |
| ANTIDIURETIC HORMONE ANTAGONISTS |
| Demeclocycline Tolvaptan |
| ANGIOTENSIN-CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS |
| Lisinopril, Enalapril, Captopril, and Ramipril |
| ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS |
| Losartan, Candesartan, Irbesartan, and Valsartan |
| DIRECT RENIN INHIBITOR Aliskiren |
| NEPHROTOXIC DRUGS |
| REFERENCES |
| Callaghan. The Renal System at a Glance. 4e. 2016. 3e. 2009. [ ataglanceseries.com/renalsystem ] Le. First Aid USMLE Step 1. Renal. 32e. 2022. 30e. 2020. Le. First Aid Basic Sciences General Principles. Renal. 3e. 2017. medimaps.co.uk/renal Been. Physiology Renal System https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL372189031E5CE5CD Najeeb. Nephrotic & Nephritic Syndrome https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLF871E4501BCECF13 Nature. http://www.nature.com/nrneph/index.html |
| MORE REFERENCES |
| Wayback Machine |